Drag Link vs. Tie Rod; Complete Comparison
Welcome to our guide on steering components: the drag link and the tie rod. These two parts play crucial roles in how your vehicle handles on the road. In this article, we’ll break down what each of them does and how they work together.
From explaining their basic functions to highlighting their importance in steering, we’ll make it easy to understand how these components impact your driving experience.
Table of Contents
What is a drag link and what does it do?
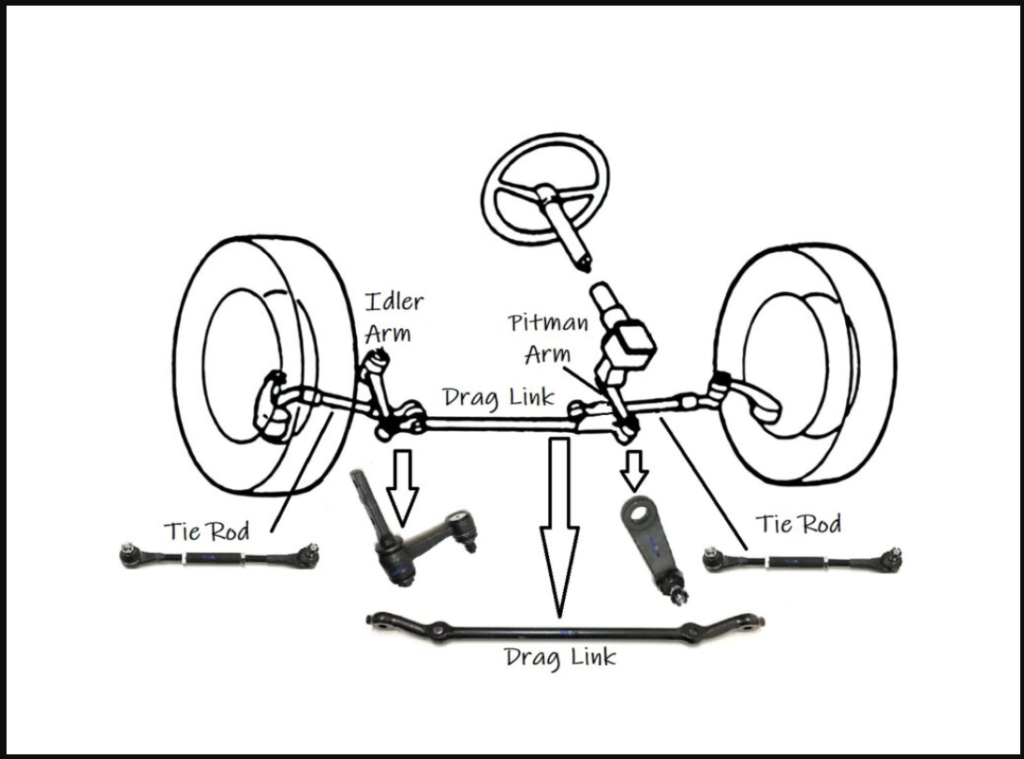
A drag link is a crucial component of a vehicle’s steering system. It is a solid metal rod that connects the steering gearbox (or steering rack) to the steering linkage or steering arm. The primary function of the drag link is to transmit the rotational movement from the steering gearbox to the steering linkage, which then moves the front wheels to steer the vehicle.
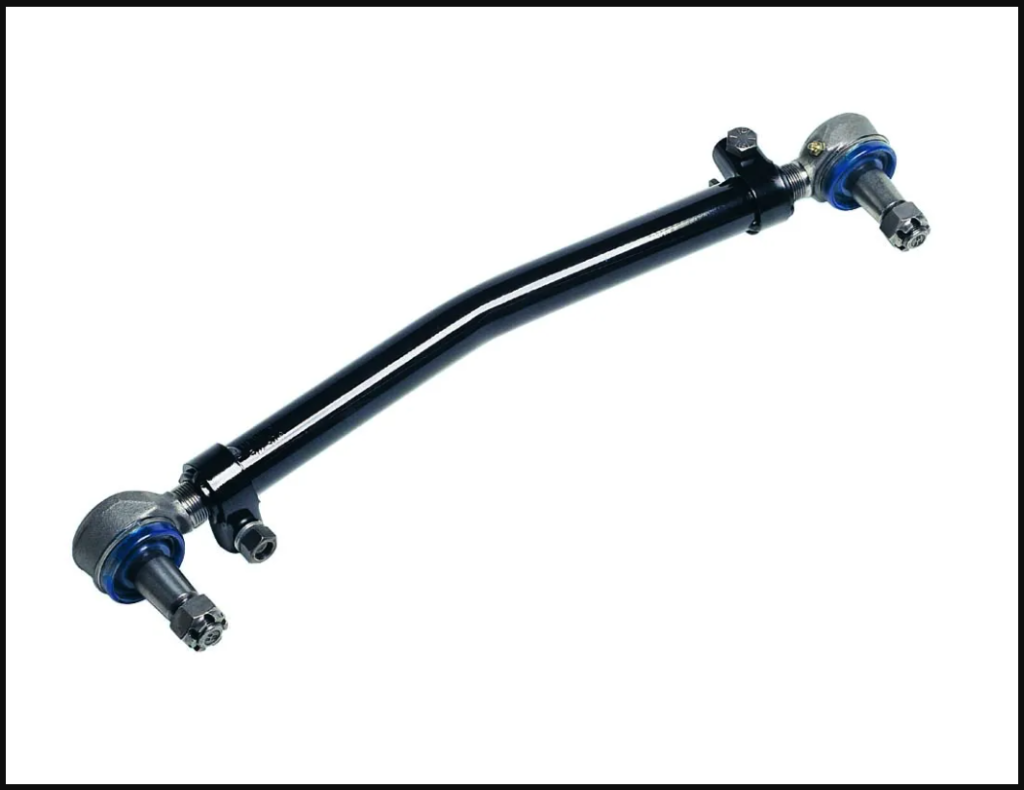

In simpler terms, when you turn the steering wheel, the rotational force is transferred through the drag link to the steering linkage, causing the wheels to turn accordingly. The drag link essentially helps to translate the driver’s input into the movement of the vehicle’s front wheels, allowing for precise steering control and direction changes while driving.
How do I know if my drag link is bad?
Detecting issues with a drag link typically involves observing signs of steering problems or abnormalities in your vehicle’s handling. Here are some indicators that your drag link may be faulty:
- Loose or Imbalanced Steering
If you notice excessive play or looseness in the steering wheel, or if the steering feels imprecise or unresponsive, it could be due to a worn-out or damaged drag link.
- Steering Wheel Vibration
Vibrations or shaking felt in the steering wheel, especially when turning or driving at higher speeds, can signal problems with the drag link or other steering components.
Can Stabilitrak Cause Car Not To Start? All You Need To Know
ENGINE RIDES
- Uneven Tire Wear
A damaged drag link can lead to improper wheel alignment, causing uneven tire wear patterns. Inspect your tires regularly for signs of uneven tread wear, which may indicate issues with the steering system.
- Clunking or Knocking Sounds
Audible noises such as clunking, knocking, or rattling when turning the steering wheel could indicate worn-out or loose components within the steering linkage, including the drag link.
- Off-Center Steering Wheel
If your steering wheel does not return to its centered position after making a turn, or if it remains off-center while driving straight, it may be a sign of drag link or alignment issues.
- Leaking Grease or Visible Damage
Inspect the drag link for any signs of physical damage, such as bends, cracks, or corrosion. Additionally, check for leaking grease around the joints or connections, which may indicate seal failure or wear.
If you notice any of these symptoms or suspect problems with your vehicle’s steering system, it’s crucial to have it inspected and repaired by a qualified mechanic or technician. Prompt diagnosis and resolution of drag link issues can help ensure safe and reliable driving performance.
How do you test a drag link?
Testing a drag link involves a series of visual inspections and manual checks to assess its condition and functionality. Here are the steps to test a drag link:
- Visual Inspection
- Begin by visually inspecting the drag link for any signs of physical damage, such as bends, cracks, or corrosion. Pay close attention to the joints, connections, and attachment points for wear or signs of looseness.
- Look for leaks around the joints or connections, which may indicate seal failure or wear in the internal components.
- Wheel Movement Test
- Raise the front of the vehicle using a jack and support it securely on jack stands.
- With the wheels off the ground, grasp each front tire at the 9 o’clock and 3 o’clock positions and attempt to rock the tire back and forth.
- Excessive movement or play in the tire could indicate issues with the drag link or other steering components.
- Visualize Drag Link Movement
- While the vehicle is still raised, visually inspect the drag link as someone else turns the steering wheel from side to side.
- Observe for any abnormal movement, such as excessive play or looseness, in the drag link or its connections.
- Drag Link End Play Test
- With the vehicle’s wheels still raised, grasp the drag link near each end and attempt to move it up and down or side to side.
- Excessive movement or play in the drag link ends may indicate worn-out or damaged components that need replacement.
- Alignment Check
- If you suspect drag link issues, it’s advisable to have the vehicle’s wheel alignment checked by a professional technician. Misaligned wheels can be a sign of drag link wear or damage.
- Professional Inspection
- If you’re uncertain about the condition of your drag link or if you suspect steering problems, it’s recommended to have the vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic or technician. They have the expertise and tools to accurately diagnose and repair drag link issues.
By following these steps and conducting a thorough inspection, you can assess the condition of your drag link and determine if any maintenance or replacement is necessary for safe and reliable driving.
What is a tie rod and what does it do?
A tie rod is another essential component of a vehicle’s steering system. It is a slender metal rod that connects the steering knuckle to the steering rack or center link. The primary function of the tie rod is to transmit the force generated by the steering system to the wheels, enabling them to turn left or right in response to the driver’s input from the steering wheel.
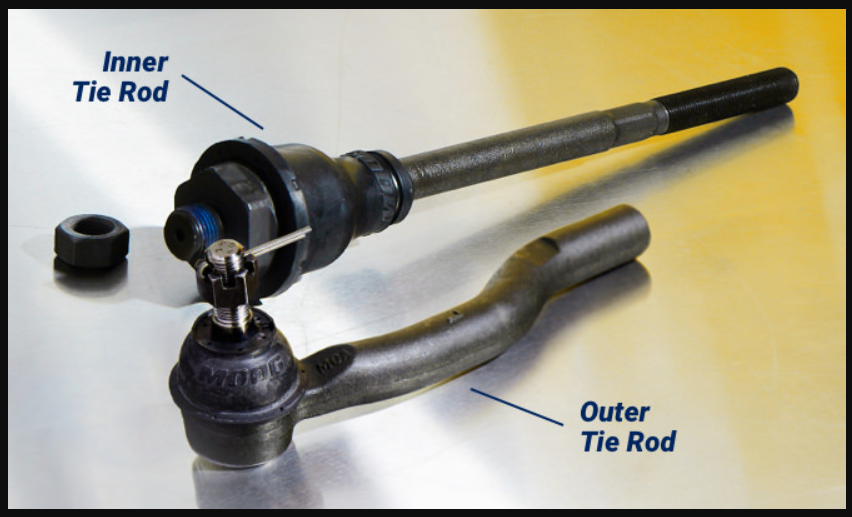
In essence, the tie rod acts as a crucial link between the steering mechanism and the wheels, ensuring that the steering motion initiated by the driver is translated accurately to the front wheels.
It helps maintain proper alignment and steering stability, allowing for controlled and precise handling of the vehicle during maneuvers and while driving straight. Proper functioning tie rods are essential for safe and predictable steering performance in any vehicle.
How do I know if my tie rod is bad?
Identifying potential issues with a tie rod involves paying attention to signs of steering irregularities or unusual handling behaviors. Here are some common indicators that your tie rod may be faulty:
- Loose or Unresponsive Steering
If you notice excessive play or looseness in the steering wheel, or if the steering feels unresponsive or imprecise, it could indicate problems with the tie rod or other steering components.
- Vibration in the Steering Wheel
Vibrations or shaking felt in the steering wheel, particularly during turns or at higher speeds, may be a sign of worn-out or damaged tie rod ends.
- Uneven Tire Wear
A faulty tie rod can lead to improper wheel alignment, causing uneven wear patterns on your tires. Inspect your tires regularly for signs of uneven tread wear, which may indicate tie rod issues.
- Clunking or Knocking Sounds
Audible noises such as clunking, knocking, or rattling when turning the steering wheel could suggest problems with the tie rod ends or other steering components.
- Off-Center Steering Wheel
If your steering wheel does not return to its centered position after making a turn, or if it remains off-center while driving straight, it may be a sign of tie rod wear or alignment problems.
- Fluid Leaks or Visible Damage
Check the tie rod for any signs of physical damage, such as bends, cracks, or corrosion. Additionally, look for leaks around the tie rod ends or joints, which may indicate seal failure or wear.
If you notice any of these symptoms or suspect issues with your vehicle’s steering system, it’s essential to have it inspected and repaired by a qualified mechanic or technician. Prompt diagnosis and resolution of tie rod problems can help maintain safe and reliable driving performance.
How do you test a tie rod?
Testing a tie rod typically involves a combination of visual inspection and manual checks to assess its condition and functionality. Here are some steps to help you test a tie rod:
- Visual Inspection
- Begin by visually inspecting the tie rod for any signs of physical damage, such as bends, cracks, or corrosion. Check the tie rod ends, joints, and connecting hardware for wear or signs of looseness.
- Look for leaks around the tie rod ends, which may indicate seal failure or wear in the internal components.
- Wheel Movement Test
- Raise the front of the vehicle using a jack and support it securely on jack stands.
- With the wheels off the ground, grasp each front tire at the 9 o’clock and 3 o’clock positions and attempt to rock the tire back and forth.
- Excessive movement or play in the tire could indicate worn-out tie rod ends or other steering components.
- Visualize Tie Rod Movement
- While the vehicle is still raised, visually inspect the tie rod ends and joints as someone else turns the steering wheel from side to side.
- Observe for any abnormal movement, such as excessive play or looseness, in the tie rod ends or joints.
- Tie Rod End Play Test
- With the vehicle’s wheels still raised, grasp the tie rod near each tie rod end and attempt to move it up and down or side to side.
- Excessive movement or play in the tie rod ends may indicate worn-out or damaged tie rod ends that need replacement.
- Alignment Check
- If you suspect tie rod issues, it’s advisable to have the vehicle’s wheel alignment checked by a professional technician. Misaligned wheels can be a sign of tie rod wear or damage.
- Professional Inspection
- If you’re unsure about the condition of your tie rods or if you suspect steering problems, it’s recommended to have the vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic or technician. They have the expertise and tools to accurately diagnose and repair tie rod issues.
By following these steps and conducting a thorough inspection, you can assess the condition of your tie rods and determine if any maintenance or replacement is necessary for safe and reliable driving.
Service Traction Control, Service Stabilitrak, Engine Power Is Reduced: Causes And Fixes Explained
ENGINE RIDES
Drag Link vs. Tie Rod; What’s the difference?
Here’s a comparison of Drag Link vs. Tie Rod, both in a descriptive format and presented in a table for clarity:
- Drag Link:
- The drag link is a solid metal rod that connects the steering gearbox (or steering rack) to the steering linkage or steering arm.
- It transmits the rotational movement from the steering gearbox to the steering linkage, causing the front wheels to turn in the desired direction.
- The drag link helps translate the driver’s input from the steering wheel into the movement of the vehicle’s front wheels, allowing for precise steering control and direction changes while driving.
- Tie Rod:
- The tie rod is a slender metal rod that connects the steering knuckle to the steering rack or center link.
- Its primary function is to transmit the force generated by the steering system to the wheels, enabling them to turn left or right in response to the driver’s input.
- The tie rod serves as a crucial link between the steering mechanism and the wheels, ensuring proper alignment, steering stability, and controlled handling during maneuvers and straight-line driving.
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Drag Link | Tie Rod |
| Function | Transmits rotational movement from steering gearbox to steering linkage | Transmits force from steering system to wheels |
| Location | Connects steering gearbox to steering linkage or arm | Connects steering knuckle to steering rack or center link |
| Construction | Solid metal rod | Slender metal rod |
| Movement | Translates steering wheel input into front wheel movement | Transmits force to turn wheels left or right |
| Importance | Essential for precise steering control and direction changes | Critical for maintaining alignment and steering stability |
| Alignment | Affects steering angle and wheel alignment | Affects wheel alignment and steering accuracy |
This comparison highlights the distinct roles and characteristics of both the drag link and tie rod in a vehicle’s steering system, emphasizing their importance for safe and controlled driving.
Conclusion
In essence, comparing the drag link and tie rod highlights their unique roles in steering systems. The drag link transmits steering wheel movement to the wheels, ensuring precise control. Conversely, the tie rod transfers force from the steering system to the wheels, enabling directional changes.
While both are vital, they differ in function and location: the drag link links the steering gearbox to the linkage, while the tie rod connects the steering knuckle to the rack or center link. Recognizing these distinctions aids in diagnosing steering issues and ensuring proper maintenance, promoting safer driving conditions overall.