The recurring failure of a car’s starter can be attributed to various factors, including electrical issues like a weak battery or faulty connections, as well as mechanical problems such as a damaged starter motor or faulty solenoid. Timely diagnosis and proper maintenance are crucial in addressing starter-related issues.
Having a reliable starter is crucial for any vehicle’s smooth operation. However, it can be incredibly frustrating when the starter keeps failing, leaving you stranded or struggling to start your car.
In this article, we will explore the reasons behind starter failures, signs to watch out for, preventive measures, and when it’s time to seek professional help.
Table of Contents
What is the Starter System, and how does it work?
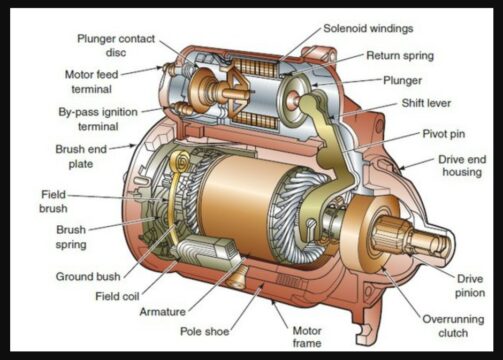
The starter is an essential component of a car’s ignition system. It is responsible for initiating the engine’s combustion process.
The system has several key elements, including the starter motor, solenoid, battery, ignition switch, and related electrical connections. When you turn the ignition key, the starter motor engages with the flywheel, rotating it and allowing the engine to start.
What causes Starter Failure?
There are some potential causes for the starter failures, and if you are experiencing problems with the starter, then take a look at the following causes.
Electrical issues
Weak battery or faulty connections: A weak battery may struggle to provide sufficient power to the starter, hindering its performance. Additionally, corroded or loose electrical connections can disrupt the flow of electricity to the starter motor.
Insufficient power supply to the starter: In some cases, the alternator may fail to charge the battery adequately, leading to a lack of power supply to the starter.
Mechanical issues
Damaged or worn-out starter motor: Over time, the starter motor’s internal components can wear out or become damaged, resulting in diminished performance or complete failure.
Faulty solenoid or starter relay: The solenoid bridges the battery and the starter motor. If it malfunctions or fails starter relay, it can prevent the starter from engaging properly.
How long should a starter last?
The lifespan of a starter can vary depending on various factors, including the make and model of the vehicle, driving conditions, and maintenance. On average, a starter can last anywhere between 80,000 to 150,000 miles (128,000 to 241,000 kilometers) or around 7 to 10 years. However, proper maintenance and timely repairs can extend its longevity.
What are the signs of a Failing Starter?
Recognizing the warning signs of a failing starter can help you address the issue before it worsens. Look out for these indicators:
Difficulty starting the engine
If you repeatedly experience trouble starting the engine, such as a slow crank or multiple attempts required to start the car, it could point to a failing starter.
Clicking sounds when turning the key
Clicking or grinding noises when turning the ignition key indicate potential issues with the starter motor or solenoid.
Frequent need for jump-starts
It could be a sign of a failing starter if you frequently need jump-starts or rely on external power sources to start your car.
Intermittent starting issues
If the starting problem occurs inconsistently, with the engine occasionally starting fine and other times not responding, it could be indicative of a faulty starter.
Maintenance and Prevention
To avoid recurring starter failures, regular maintenance and preventive measures are essential:
- Regular battery inspections and maintenance: Ensure the battery is in good condition, check its voltage regularly, and clean any corrosion on the terminals.
- Checking and cleaning electrical connections: Periodically inspect the connections between the battery, starter motor, and solenoid. Clean any corrosion or tighten loose connections.
- Addressing warning signs promptly: If you notice any signs of a failing starter, such as slow cranking or clicking sounds, have it inspected by a professional as soon as possible.
- Professional maintenance and servicing: Schedule regular maintenance with a trusted mechanic who can diagnose and address potential issues before they escalate.
Is it worth replacing a starter? And how to replace the starter?
Replacing a starter is usually worth it if your current starter is malfunctioning or has failed. It’s more cost-effective to replace the starter than to continue experiencing starting issues or being stranded due to a non-functioning starter. Here are the general steps to replace a starter (specific steps may vary depending on the vehicle):
- Safety first: Park the vehicle on a flat surface, engage the parking brake and disconnect the battery’s negative terminal to prevent electrical accidents.
- Locate the starter: The starter is typically located near the engine and is attached to the transmission bell housing.
- Remove connections: Label and disconnect all electrical connections from the starter, including the main power cable and smaller control wires. Remember their positions for reinstallation.
- Remove mounting bolts: Loosen and remove the mounting bolts that secure the starter to the engine or transmission. Keep track of their locations and any shims present.
- Remove the old starter: Gently pull the old starter away from the engine, not damaging surrounding components.
- Install the new starter: Position it in place, aligning it with the mounting holes. Reinstall the mounting bolts, ensuring they are tightened securely.
- Reconnect electrical connections: Attach the main power cable and any control wires to their respective terminals on the new starter, following the labels made during removal.
- Double-check: Ensure all connections are secure and the starter is properly aligned. Reinstall any shims if necessary.
- Reconnect the battery: Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Test the new starter: Turn the ignition key to start the engine and verify that the new starter engages smoothly.
Suppose you’re unsure about performing the replacement yourself. In that case, it’s advisable to seek the assistance of a professional mechanic who can ensure proper installation and address any additional issues that may arise during the process.
Can you test a starter? and how?
Yes, a starter can be tested to determine its functionality. Here’s a common method for testing a starter:
- Safety precautions: Ensure the vehicle is in park or neutral with the parking brake engaged, and the ignition is off. Also, disconnect the battery’s negative terminal to prevent any electrical accidents.
- Locate the starter: The starter is typically mounted on the engine, near the transmission bell housing. Refer to the vehicle’s manual if needed.
- Inspect connections: Examine the electrical connections on the starter, including the main power cable and any smaller control wires. Ensure they are secure and free from corrosion or damage. Clean or repair connections as necessary.
- Voltage test: Use a multimeter set to DC voltage and connect the positive lead to the starter’s main power terminal and the negative lead to a good ground, such as the engine block or chassis.
- Check battery voltage: Have someone turn the ignition key to the “start” position while you observe the multimeter. Ideally, the voltage should remain above 10 volts during cranking. If the voltage drops significantly or falls below 10 volts, it indicates a weak battery or high resistance in the circuit.
- Starter motor test: If the battery voltage remains sufficient during cranking, it’s time to test the starter motor itself. Use a remote starter switch or have an assistant turn the ignition key while you monitor the starter’s operation.
- Listen for unusual noises: If the starter emits grinding, screeching, or clicking sounds, it may indicate a faulty starter motor or solenoid.
- Observe the starter’s operation: The starter motor should consistently engage and spin the engine’s flywheel. If it struggles to engage or spins slowly, it suggests a problem with the starter motor.
Remember, these steps provide a general guideline for testing a starter. It’s recommended to consult the vehicle’s manual or seek professional assistance for specific instructions and troubleshooting tailored to your car’s make and model.
When to Seek Professional Help?
While some DIY troubleshooting is possible, there are limitations to what an average car owner can do. Seeking professional help is advisable under the following circumstances:
- Lack of technical expertise or tools required for in-depth diagnostics and repairs.
- Persistent starter issues despite attempts at DIY troubleshooting.
- Concerns about warranty coverage or potential complexities involved in starter system repairs.
Conclusion
A properly functioning starter is vital for a reliable and hassle-free driving experience. Understanding the causes of starter failures, recognizing the warning signs, and prioritizing regular maintenance can help prevent recurring issues. Remember, when in doubt, it’s best to consult a professional to diagnose and address any problems with your car’s starter system. By staying proactive, you can minimize the inconvenience and expenses associated with starter failures, ensuring a smooth start every time you turn the key.







One Comment